Fiber Laser Welding Machine: Steel, Titanium Welding
Source:razorteklaser Time:2025-11-04
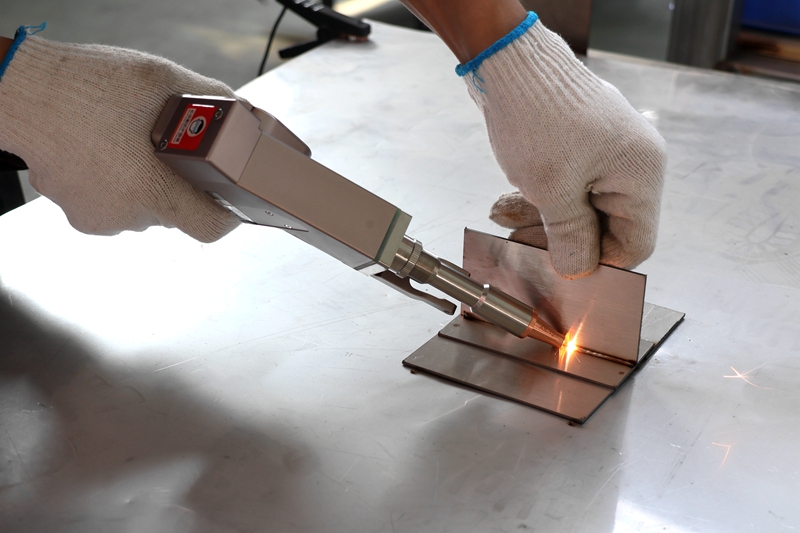

Fiber laser welding machines are widely used in modern manufacturing due to their advantages of good beam quality, high efficiency, and high precision. It can weld a wide variety of metal materials, covering almost all common engineering metal materials. The types of metals that can be welded include stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper, carbon steel, titanium alloy, etc.
Steel Welding
Steel is the most widely used field for fiber laser welding:
1. Carbon steel/low carbon steel
Characteristics: Excellent welding performance, making it one of the most ideal materials for laser welding.
Applications: automotive body, chassis, household appliances, steel structures, etc.
Key point: The lower the carbon content, the better the weldability. Attention should be paid to controlling the heat input to avoid coarse grains and decreased strength.
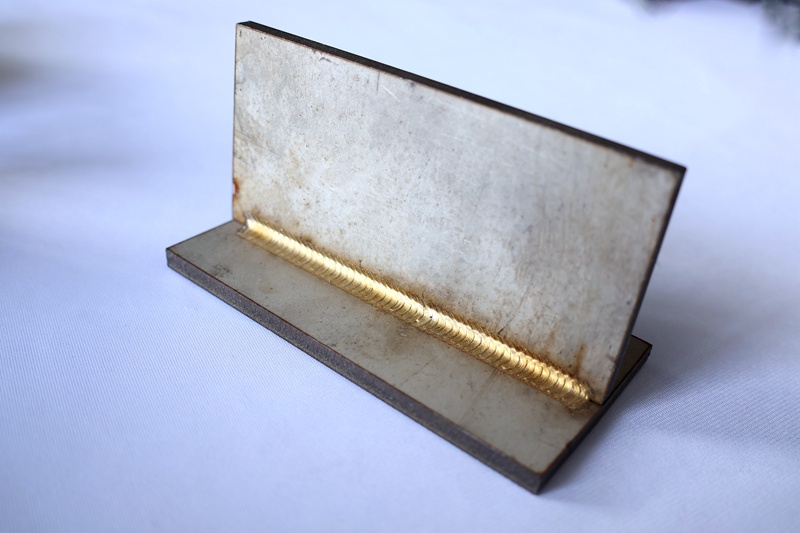

2. Stainless steel
Austenitic stainless steel (such as 304, 316): has good weldability, but attention should be paid to preventing carbide precipitation from causing a decrease in corrosion resistance. The high speed and low heat input of laser welding are very advantageous for this.
Ferritic stainless steel (such as 430): The weldability is acceptable, but the grains in the heat affected zone are prone to grow, which may lead to a decrease in toughness and corrosion resistance.
Martensitic stainless steel (such as 420): Poor weldability, tendency for quenching and cold cracking, usually requiring preheating and post heating.
Applications: Kitchen equipment, medical devices, food industry, chemical containers, precision parts.
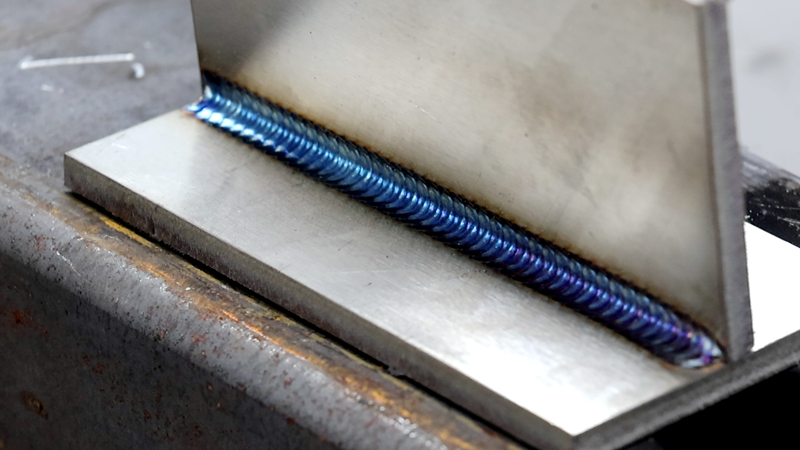

Titanium and Titanium alloys Welding
Characteristics: High strength, light weight, corrosion resistance, but active chemical properties, easily reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen at high temperatures, leading to weld embrittlement.
Key requirement: Welding must be carried out under the protection of high-purity inert gas (such as 99.999% argon gas), and the protection range should cover both the front and back of the molten pool.
Applications: Aerospace, military, medical implants (such as artificial joints).