Application case of laser welding in medical device production
Source:razorteklaser Time:2025-07-11
Laser welding is widely used in the production of medical devices. Its core advantages are high precision, low heat input, non-contact, weldable refractory metals and heterogeneous materials, easy automation, and clean and pollution-free welds. These characteristics perfectly meet the stringent requirements of medical devices for precision, reliability, biocompatibility and sterility.
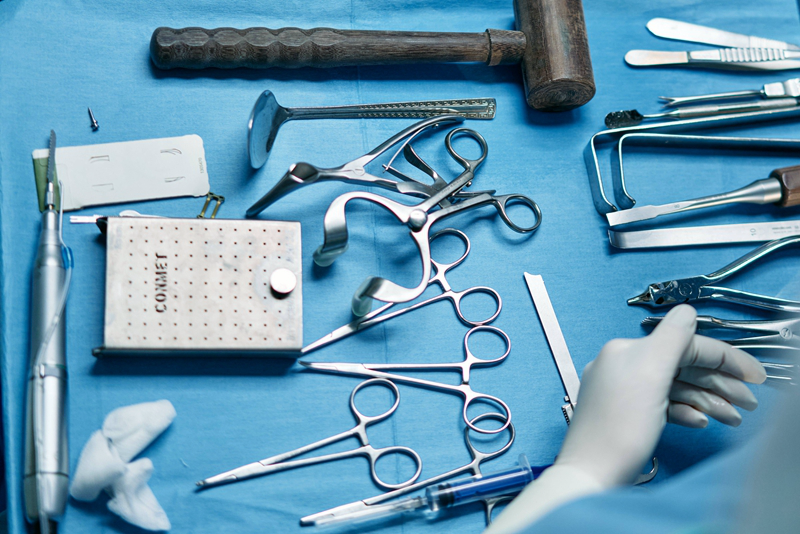

Here are some typical application cases:
1. Seal welding of the shell of implantable electronic medical devices (pacemakers, nerve stimulators, implantable sensors, etc.):
This is one of the most classic and key applications of laser welding in medical devices. The shell of these devices (usually made of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V or special stainless steel such as 316LVM) needs to be completely sealed to protect the internal precision electronic components from the corrosion of receptor fluid and ensure the biocompatibility of long-term implantation.
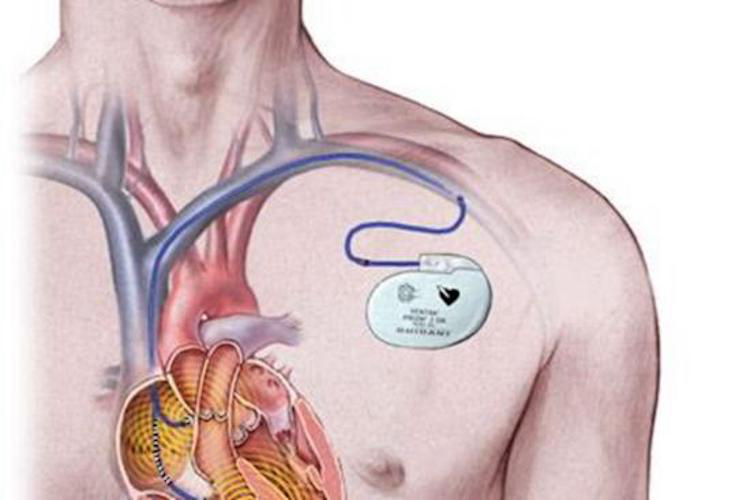
Advantages of laser welding:
Precision sealing: produce extremely narrow and depth controllable welds to achieve a real sense of air tight and liquid tight sealing.
Low heat input: minimize the heat affected zone and avoid damage to internal temperature sensitive components (such as batteries and chips).
Material applicability: it is very suitable for welding titanium alloy (with good biocompatibility and corrosion resistance) and special stainless steel.
No additive material: self fusion welding is usually used without welding wire to avoid the introduction of foreign substances and ensure the purity and biocompatibility of the weld.
Automation and consistency: highly automated to ensure the quality and consistency of welds in mass production.
Smooth weld: reduce subsequent cleaning and polishing processes and reduce pollution risk.
2. Endoscopes and minimally invasive surgical instruments: Welding slender tubular structures (such as mirror tube, instrument channel), complex articulated structures, small stainless steel or titanium alloy parts (such as jaw, cutter head).
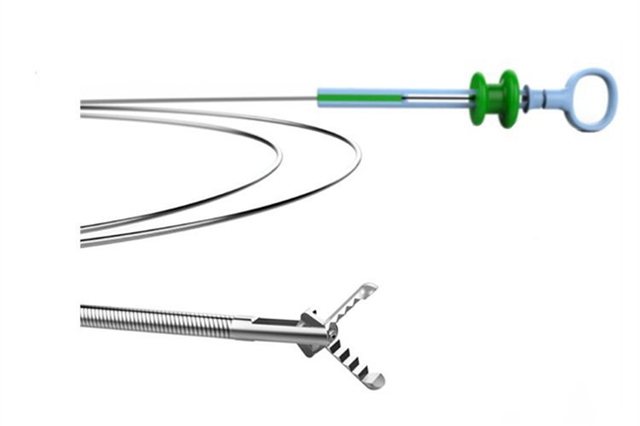
Advantages of laser welding:
Micro welding ability: it can weld very small parts (such as parts with diameter less than 1mm) to meet the needs of device miniaturization.
Precise positioning: the laser beam can accurately locate the hard to reach area and weld complex geometry.
Low deformation: low heat input, greatly reducing the deformation of thin-walled pipe fittings and fine structures, ensuring the accuracy and flexibility of instruments.
High strength joint: it provides a firm and reliable connection and bears the force and torque in the operation.
Clean without spatter: the weld is clean without spatter, so as to avoid the risk of residual pollution inside the device and simplify the cleaning and disinfection process.
3. Hemodialyzer and oxygenator:
Weld the shell, end cap and the end plate (usually polypropylene or engineering plastic) of the complex polypropylene hollow fiber membrane bundle inside. Although other lasers (such as semiconductor laser and diode laser) are commonly used in plastic welding, the welding of precision metal parts still relies on solid-state laser or fiber laser.
Advantages of laser welding:
Reliable sealing: ensure the complete isolation of blood flow path and dialysate flow path to prevent cross contamination.
Material compatibility: suitable for welding engineering plastic (laser transmission welding) or metal parts commonly used in dialyzer shell.
Non contact welding of plastic fibers: for the end fixation and sealing of plastic hollow fiber bundles, laser welding provides a non-contact, low stress method (especially suitable for laser transmission welding process).
4. Surgical instruments (pliers, scissors, needle holder, bone drill, electric knife head, etc.): welding the connection between blade and handle, movable joint, stainless steel or titanium alloy parts, replacement head end, etc.
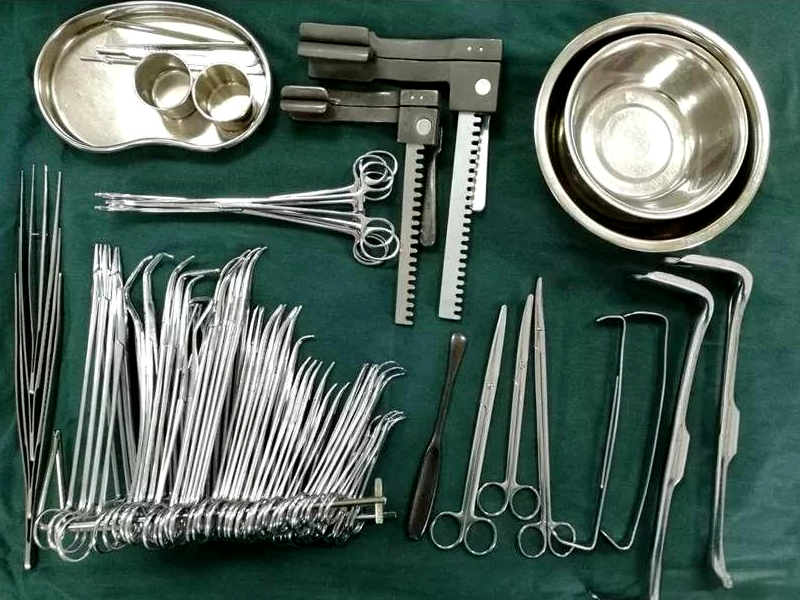
Advantages of laser welding:
High strength and durability: produce high-strength welds to ensure the reliability of instruments in repeated disinfection and surgical use.
Precise connection: maintain the precise alignment and sharpness of instruments (especially scissors and needle holders).
Low deformation: minimize thermal deformation and ensure the dimensional accuracy and operation feel of the instrument.
Welding of different materials: sometimes it is necessary to weld different materials (such as stainless steel and carbide bit) together.
The weld is smooth and easy to clean: the smooth weld surface is convenient for thorough cleaning and sterilization.
5. Dental implants and restorations: Welded pure titanium or titanium alloy implant abutments, personalized abutments, dental bridge brackets, denture frames, etc.
Advantages of laser welding:
Biocompatibility guarantee: high quality and pollution-free welding ensures the biocompatibility of titanium implants.
Precision processing: meet the extremely high requirements of dental restorations for accuracy and adaptability.
Low heat input: avoid damage of implant surface modification layer (such as sand blasting and acid etching treatment layer) due to overheating.
Repair and personalization: it is very suitable for repairing fractured restorations or making highly personalized implant superstructure.
6. Orthopedic implants (bone plates, bone nails, spinal instruments):
Although electron beam welding or plasma welding are mainly used for large implants, laser welding is applied to the welding of small, complex or precision positioning components (such as locking hole accessories, connectors, customized implants).
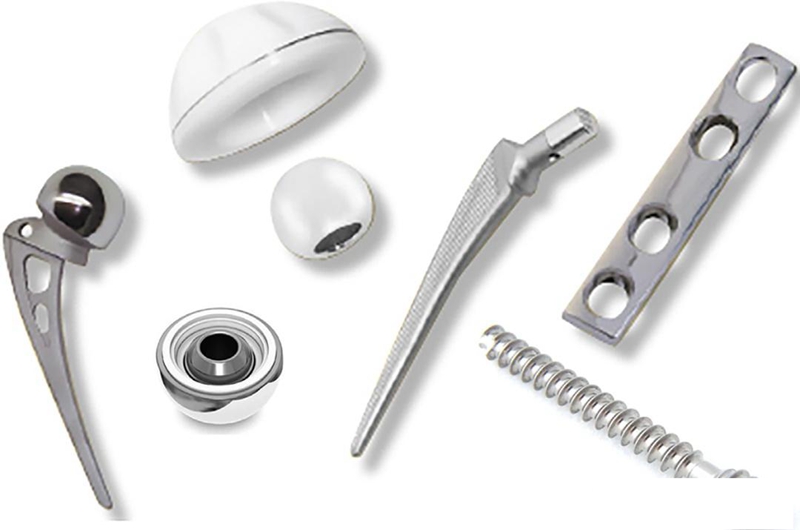

Advantages of laser welding:
Local welding: precise welding can be carried out at the specific position of the processed implant without affecting the overall performance.
Low heat input: reduce the impact on the overall mechanical properties and microstructure of the implant.
Complex geometry: welding areas that are difficult to access by traditional methods.
7. Sensor and conduit components: weld tiny sensor housings (such as pressure sensors, temperature sensors), conduit tip components, guide wires, connectors, etc.
Advantages of laser welding:
Ultra micro welding: s uitable for extremely small metal parts (micron level).
Precise control: precisely control the heat input and welding position to protect sensitive elements.
Material diversity: it can weld stainless steel, nickel titanium alloy, platinum iridium alloy and other commonly used medical metals.
Key considerations for laser welding technology:
1. Process parameter optimization: power, speed, frequency, defocus, shielding gas, etc. need to be accurately optimized for specific materials and geometric shapes.
2. Cleanliness: the workpiece must be thoroughly cleaned before welding to remove grease, oxides and other pollutants, otherwise the welding quality and biocompatibility will be seriously affected.
3. Fixture design: precision fixture is very important to ensure the accurate positioning and gap control of micro parts.
4. Process monitoring: coaxial camera, molten pool monitoring, plasma monitoring and other technologies are used to monitor the welding quality in real time.

Verification and compliance:
strict verification (process verification, equipment verification) must be carried out to ensure that the weld meets the requirements of mechanical properties, sealing, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility and other requirements, and conforms to the quality management system and regulatory requirements of medical devices such as ISO 13485 and FDA QSR.
Laser welding has become an indispensable key technology for modern high-end medical device manufacturing. By providing unparalleled accuracy, controllability, cleanliness and reliability, it meets the strict requirements for extreme performance, safety and long-term stability of medical devices, especially implantable and invasive devices. With the continuous progress of laser technology and automation, its application in the field of medical devices will be more in-depth and extensive.
